Information about increasing IT-awareness
Cyber security begins with every user’s behaviour on the Internet.
Remember the basic rules of safe behaviour:
| |
- Use different strong passwords in different environments.
|
| |
- Use a PIN in your computer whenever possible.
|
| |
- If the environment allows, definitely use two-factor authentication.
|
| |
- Update your passwords regularly and do not share them with anyone else.
|
| |
- Do not publish your personal information or share it with strangers.
|
| |
- Do not open letters, links and attachments from unknown origin. If someone you know sends you a link or attachment with a different method of communication and/or text, always double check what it is. If you are unsure, check whether the e-mail address and name are correct.
|
| |
- Make sure that the web page where you have to enter personal information is protected with a secure encrypted connection: there should be https at the beginning of the address.
|
| |
- Try to avoid using shared and public devices. If that is not possible, make sure to always log out from all the sites you have visited or logged into. Whenever possible, also use the “private” or “incognito“ mode.
|
Recommendations for creating passwords
| |
- A password should be long (at least 8 characters). Use a pass phrase instead of a password.
|
| |
- A password / pass phrase must not be easily guessed (e.g. the first name and surname or birthday of a family member).
|
| |
- Use a password manager. That helps you generate a unique strong password for each web page and thus reduces the risk that several of your user accounts are jeopardized when one password leaks. That also saves you the trouble of remembering passwords and simplifies logging into web pages, automatically filling in the user name and password fields for you. The most popular password managers are, for instance, LastPass, Bitwarden, 1Password, Dashlane and KeePass.
|
How to protect your user accounts?
Rules for protection of your user accounts:
| |
- exchange the default password of a device or service (initial password) with a new secure password
|
| |
- change passwords regularly
|
| |
- do not reuse the same password in different services
|
| |
- choose a strong and easily memorized password, do not write it down or share it with other people
|
| |
- if you suspect that your password has been revealed to unauthorised persons (even if it is someone you know well), replace it at once
|
| |
- use two-factor authentication in all the environments where it is possible. Two-factor authentication is also logging in with ID card, mobile ID or Smart ID.
|
Malware
Malware is software the purpose of which is to harm your device.
For instance to encrypt the data and demand money for decryption, use the resources of your computer for mining cryptocurrency (that naturally someone else receives), steal information from your device or add your device to a robot network in order to use it later on for carrying out attacks.
For protection against malware:
| |
- Do not open attachments or web links received from unknown senders.
|
| |
- Do not believe threatening letters that require quick action from unknown senders you have never heard of before or never had anything to do with.
|
| |
- Do not insert unknown USB memory sticks into your computer.
|
Phishing pages
The purpose of phishing pages is to steal your data. When phishing pages are created, the greatest focus is on making the page look like the real brand, making you feel like you are on the legitimate page.
Before you enter your data in any web page:
| |
- Make sure that every letter of the URL you are visiting is what it should be (google.com vs g00gle.com).
|
| |
- If unsure, open a search engine in another window and enter the name of the desired environment. The official web page of the actual brand is always displayed first in search engines.
|
| |
- To make sure the URL is legitimate, you should read the address not from left to right but two characters left from the leftmost slash on the URL bar. For instance, when looking at URL facbook.com.popsi7.com/fbc/security.php, you can thus see that it is not Facebook at all but a page called popsi7.com. When reading from the left, the first ones to be displayed are subdomains, e.g. mail.google.com denotes Gmail, the e-mail service of Google.
|
| |
- If you have accidentally entered your user information into a phishing page:
- immediately change the password of your account
- make sure you have activated two-factor authentication
|
Phising e-mail
| |
- Phishing e-mails may seemingly come from top executives of companies!
|
| |
- The e-mail may request a bank transfer or forward bank account information, a password, etc.
|
| |
- The e-mail may contain a file with “very important” information requiring a quick response.
|
| |
- The e-mail may look a lot like the working files of a user (a price list, invoice, presentation, zip-file, pdf-file).
|
| |
- E-mails promising money or trips are highly likely to be fraudulent.
|
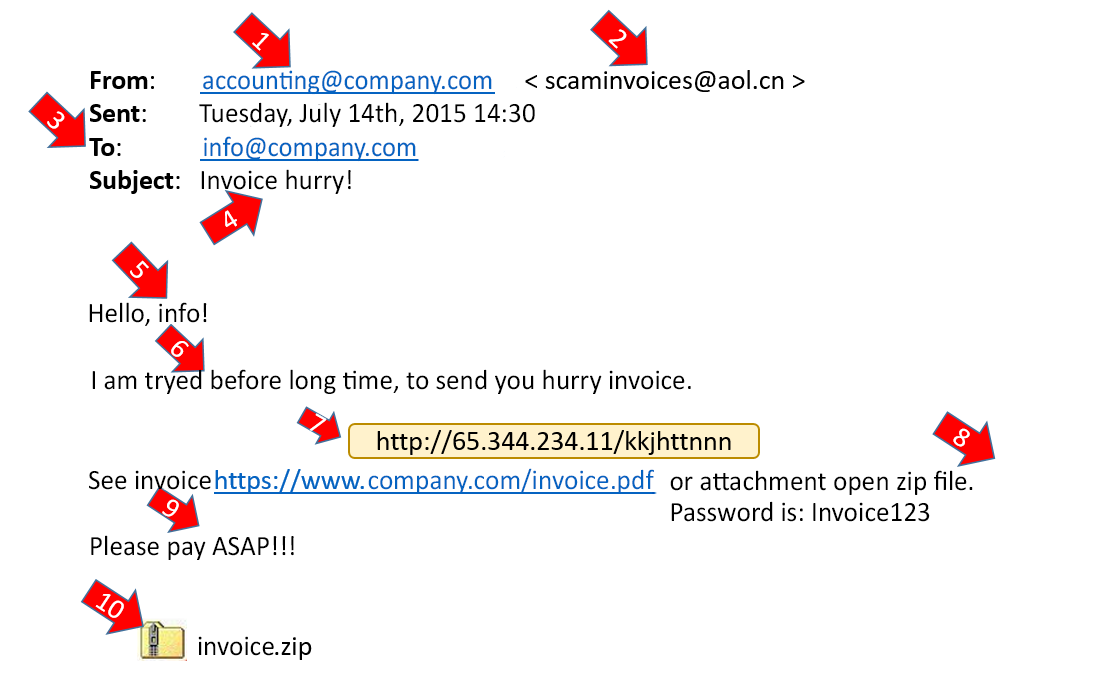
How to identify?
| |
|
| |
- the sender’s e-mail address,
|
| |
- the e-mail address of the recipient,
|
| |
- check the title and content of the e-mail – it does seem suspicious, doesn’t it?
|
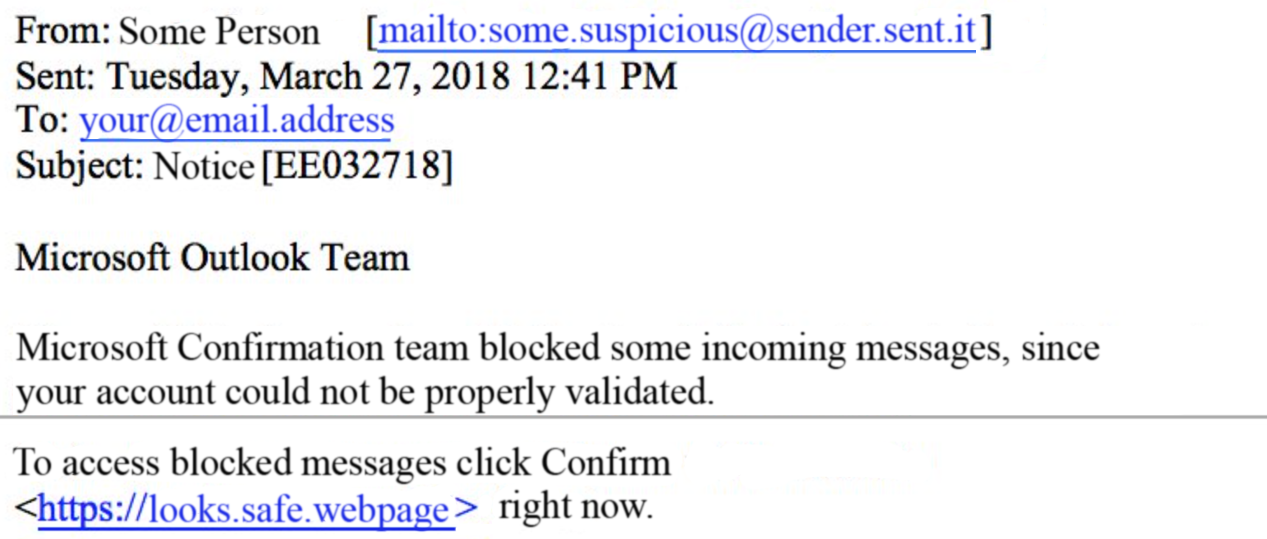
What to do?
| |
- Do not open any attachments or click any links, do not reply to the e-mail.
|
| |
- If you have any doubts, ask the sender to confirm that they sent the e-mail, or contact your IT support / forward the letter to the IT manager.
|
| |
- Delete the e-mail with suspicious content.
|
Security of smart devices
What to do to keep your smart devices secure?
| |
- Use the latest software version in your smart device. Make sure you have automatic security updates turned on.
|
| |
- Only download phone apps from the official store of the producer (Google Play Store, Apple App Store and Windows Store). When you download apps, also check the information of the app developer and user feedback.
|
| |
- Check the privacy settings of the app (also after updates) and double check which information the apps can access in the phone.
|
| |
- Use the key lock to protect your phone and privacy. A password / security code can also be installed for apps in order to better protect your personal information. Do not use the most widespread simple patterns or number combinations for the key lock.
|
| |
- Do not open letters, links and attachments from unknown origin in your mobile device. If someone you know sends you a link or attachment with a different method of communication and/or text, always double check what it is. As smart devices substitute the conventional computer for many people, there is also malware specially designed for smart devices.
|
| |
- If possible, use mobile data instead of Wi-Fi in public places. At least once every six months, remove the unnecessary Wi-Fi networks, so that your phone would not connect to a malicious Wi-Fi network with the same name.
|
| |
- To avoid losing important contacts and files, make regular back-up copies of the files and information in your phone to a memory card in your phone or an account connected with your phone.
|
| |
- For added security, if possible, encrypt the whole content of the phone (under Settings), so that the information in the phone would not end up in unauthorised hands.
|
If you suspect that you have accidentally made a mistake in any of the items listed above, inform your IT partner of that as soon as possible or send an e-mail to tugi@primend.ee call us on +372 687 0606
Ask for an offer


